Recently, Zhang Hanyue, a young teacher at the School of Bioscience and Medical Engineering of Southeast University, achieved ferroelectric imprinting on a biodegradable polylactic acid film for the first time. The relevant research results are titled “For the first time on a biodegradable polylactic acid film” Observation of ferroelectric imprinting
of ferroelectric lithography on biodegradable PLA films” was published in the journal “Advanced Materials”
Materials” on.
Ferroelectric imprinting technology is a high-precision processing technology that can purposefully design and control ferroelectric domains at the micro/nano scale. It is widely used in non-volatile memories, sensors, field effect transistors, track memories, and photodetectors. It has very important applications in other fields. The technology is similar to movable type printing, in which the probe of a piezoelectric force microscope (PFM) can act like a “pen” by applying voltage to the “paper” of ferroelectric material to draw the desired domain pattern. At present, research on ferroelectric imprinting technology mainly focuses on inorganic ceramics and organic polymers. However, inorganic ceramics themselves have shortcomings such as rigidity and difficulty in film preparation. Organic ferroelectric polymers have good mechanical flexibility, but they are not suitable for ferroelectric imprinting. The research mainly focuses on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and its copolymers, which have complex stretch polarization processes and are difficult to biodegrade.
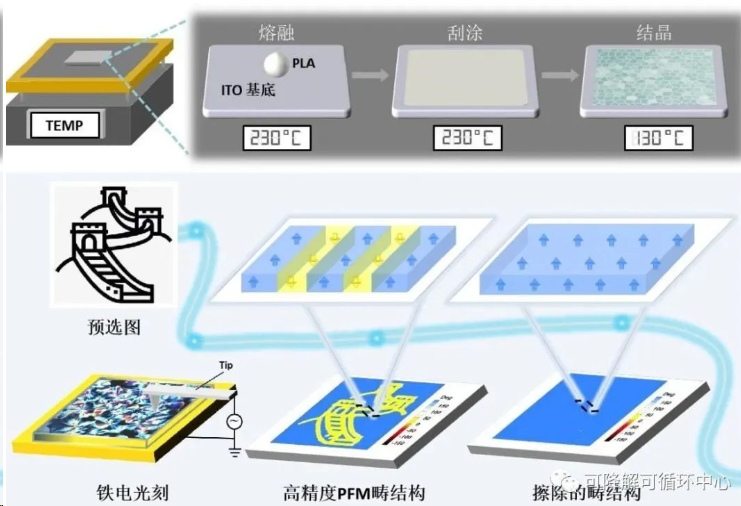
The preparation process of semi-crystalline PLA film (top) and its ferroelectric imprinting diagram (bottom)
Zhang Hanyue’s team used the “ferroelectric chemistry” theory proposed by Professor Xiong Rengen to explore the ferroelectric nanoimprinting behavior based on biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA) films. The team prepared a PLA film with room temperature ferroelectricity and ferroelectric imprinting capabilities through a simple melt-casting method and under simple conditions without stretching and high-voltage polarization. By applying a local electric field of a specific size, ferroelectric polarization reversal can be achieved on a PLA film at room temperature; it is particularly noteworthy that the ferroelectric domain structure can also be accurately written on the surface of the PLA film according to a predetermined pattern. Enter and erase. It is reported that PLA is the first biocompatible and biodegradable organic ferroelectric polymer. The discovery of its room temperature ferroelectricity and ferroelectric imprinting ability is of great significance for biomedicine and bioelectronics applications, especially for Implantable transient electronic medical devices.
Master student Jiang Huanhuan from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Southeast University and Dr. Song Xianjiang, a young teacher from Nanchang University, are the co-first authors of the paper. Professor Xiong Rengen and Associate Researcher Zhang Hanyue from Southeast University are the co-corresponding authors, and Southeast University is the first corresponding unit. This work was strongly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

